Learn the Fundamental Analysis – Find best Stocks
- “Discover the influence of stock fundamental analysis in predicting market trends. Explore how analyzing key financial metrics empowers investors to make informed decisions and navigate the stock market landscape with confidence.”
Introduction:
- Welcome to the exciting world of stock fundamental analysis, where numbers reign supreme and every data point tells a story about the future of the market. But don’t worry, you don’t need to be a math whiz to understand how fundamental analysis works.
- In this article, we’ll explore how the power of numbers can be harnessed to predict market trends and maybe even make you a few bucks along the way. So, pick up your arithmetic tool and let’s plunge into the depths.
What is Fundamental Analysis?
- Fundamental analysis serves as a strategic tool employed by investors to assess a stock’s true worth. Diverging from technical analysis, which scrutinizes price shifts and graphical trends, fundamental analysis delves deeper into a company’s financial well-being and operational prowess..
- By scrutinizing key metrics such as earnings, revenue, assets, and liabilities, investors can gain insights into the true worth of a stock.
The Basics of Fundamental Analysis: What’s Under the Hood?
- Unraveling the intricacies of fundamental analysis is akin to peering beneath the surface of a puzzle to unveil the authentic worth of a stock. It involves digging into a company’s financial statements, earnings reports, and economic indicators to assess its health and growth potential
The Foundation: Understanding Key Financial Ratios
- Ever heard of PE ratio, EPS, or ROE and felt like you were drowning in alphabet soup? Fear not! These are just some of the key financial ratios that fundamental analysts use to evaluate a company’s performance and valuation.
- Think of them as the building blocks of financial analysis – once you understand them, the rest falls into place.
Key Metrics in Fundamental Analysis
Earnings Per Share (EPS) :
- EPS stands as a fundamental gauge, quantifying a company’s profit potential. The computation involves dividing the net income by the total count of outstanding shares. A higher EPS indicates greater profitability and potential for growth.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
- The P/E ratio juxtaposes a company’s prevailing stock price against its earnings per share, serving as a popular barometer for stock valuation. A lofty P/E ratio might hint at potential overvaluation, whereas a modest P/E ratio could signal an undervalued stock.
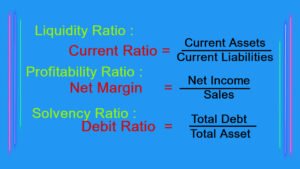
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- The debt-to-equity ratio assesses a company’s financial leverage by comparing its total debt to its shareholders’ equity. A lower ratio indicates a healthier balance sheet, as it signifies lower reliance on borrowed funds to finance operations.
Return on Equity (ROE)
- ROE quantifies a company’s profit efficiency concerning its shareholders’ equity, showcasing the efficacy of its equity employment in profit generation. A higher ROE is generally preferred, as it signifies efficient capital utilization.
Earnings Reports: The Stock Market’s Report Card
- Picture this: it’s earnings season, and companies are lining up to show off their quarterly report cards. For fundamental analysts, these reports are like Christmas morning – full of surprises, excitement, and the occasional disappointment.
- By analyzing revenue, profit margins, and guidance, analysts can gauge a company’s health and predict its future trajectory.
Economic Indicators: Reading the Tea Leaves of the Economy
- Ever wondered why the stock market reacts to seemingly random economic reports like GDP growth or unemployment figures? It’s because these indicators provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy, which in turn affects corporate earnings and stock prices.
- It’s like trying to predict the weather – except instead of rain or shine, you’re forecasting market booms and busts!
The Art of Forecasting: Predicting Market Trends
- Armed with a treasure trove of data, fundamental analysts play the role of fortune tellers, using their insights to predict future market trends.
- By identifying undervalued stocks with strong growth potential or spotting warning signs of impending downturns, analysts can help investors make informed decisions and hopefully avoid financial disasters.
Predicting Market Trends with Fundamental Analysis
- By analyzing these key metrics and assessing the overall financial health of a company, investors can make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks.
- Fundamental analysis enables investors to identify undervalued stocks with strong growth potential or overvalued stocks that may be ripe for a correction.
- Moreover, fundamental analysis provides a long-term perspective, allowing investors to weather short-term market fluctuations and focus on the underlying value of their investments.
- By taking a disciplined and analytical approach, investors can mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities in the ever-changing stock market landscape.
- In the whirlwind realm of investment, grasping the intricacies of stock market dynamics is paramount. While many factors come into play, fundamental analysis stands out as a powerful tool for predicting market trends.
- In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of fundamental analysis and explore how it harnesses the power of numbers to foresee market movements.
The Role of Financial Statements
- Central to fundamental analysis are a company’s financial statements, namely the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. These documents provide a snapshot of the company’s financial performance, revealing vital information about its profitability, liquidity, and solvency.
- Analysts pore over these statements to assess the company’s past performance and make projections about its future prospects.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, the power of numbers in stock fundamental analysis cannot be overstated. By delving into financial statements and scrutinizing key metrics, investors can gain valuable insights into the true worth of a stock.
- Armed with this knowledge, they can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the stock market with confidence. So, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, harness the power of fundamental analysis to unlock the potential of your investments.
- And there you have it – a crash course in the power of numbers and how fundamental analysis can be used to predict market trends. So, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just dipping your toes into the world of finance, remember that behind every stock price is a story waiting to be told.
- So, crunch those numbers, trust your instincts, and who knows? Maybe you’ll be the next Warren Buffett – or at least make enough to treat yourself to a fancy dinner!
Frequently Asked Questions:

What is fundamental analysis?
Answer:
- Fundamental analysis is a method of evaluating a company’s intrinsic value by analyzing its financial statements, earnings reports, and economic indicators to assess its health and growth potential.
What are some key financial ratios used in fundamental analysis?
Answer:
- Key financial ratios include the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, earnings per share (EPS), return on equity (ROE), and debt-to-equity ratio.
- These ratios help analysts gauge a company’s profitability, efficiency, and financial stability.
How do earnings reports impact stock prices?
Answer:
- Earnings reports provide insights into a company’s performance, including revenue, profit margins, and future guidance.
- Positive earnings surprises often lead to stock price increases, while negative surprises can result in price declines as investors adjust their expectations.
What role do economic indicators play in fundamental analysis?
Answer:
- Economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer spending data provide insights into the overall health of the economy.
- Fundamental analysts use these indicators to assess the broader market environment and predict how it may impact corporate earnings and stock prices.
How do fundamental analysts forecast market trends?
Answer:
- Fundamental analysts use a combination of financial data, economic indicators, and industry trends to forecast market trends.
- By identifying undervalued stocks with strong growth potential or warning signs of downturns, analysts aim to help investors make informed decisions.
What are the advantages of fundamental analysis?
Answer:
- Fundamental analysis provides a long-term perspective on investment opportunities, focusing on the underlying value of a company rather than short-term market fluctuations.
- It helps investors identify quality stocks with strong fundamentals and growth potential.
Are there any limitations to fundamental analysis?
Answer:
- One limitation of fundamental analysis is that it requires access to accurate and up-to-date financial information, which may not always be readily available.
- Additionally, fundamental analysis does not account for short-term market sentiment or speculative behavior.
How can investors use fundamental analysis in their investment strategy?
Answer:
- Investors can use fundamental analysis to identify undervalued or overvalued stocks, assess the financial health of companies, and make informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling investments.
- It serves as a valuable tool for long-term investment planning.
Can fundamental analysis be applied to different types of assets?
Answer:
- Yes, fundamental analysis can be applied to various assets, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies.
- The principles of fundamental analysis remain the same, focusing on assessing the intrinsic value of an asset based on its underlying fundamentals.
Is fundamental analysis suitable for all investors?
Answer:
- Fundamental analysis requires a thorough understanding of financial statements, economic indicators, and industry dynamics, which may not be suitable for all investors.
- It is often used by long-term investors who are willing to conduct in-depth research and analysis. Short-term traders may rely more on technical analysis for their investment decisions.